How Does an FDM 3D Printer Work: Complete Guide 2024
Have you ever entered a modern printing shop and chances are you see an iconic device — a boxy frame 3D printer? Layer-by-layer printing is fabricating the substrate like a robotic spider web. You’re still in shock to know what’s the magic behind
In the 21st century, the technology has come a long way. It’s the magic of FDM 3D printing, one of the most widely used 3D printing technologies. That’s why FDM printers rule the market for their features, simplicity, affordability, versatility, and high creative freedom.
Whether you are a hobbyist, an educator, or a professional in the manufacturing industry, FDM 3D printers can guide you on a tool path to create everything from the prototypes to the end-use parts.
From dentistry to jewelry, education, science, and interior design art, FDM 3D printers can handle it all, both on a desktop and industrial scale. A new invention in town is the tattoo stencil printer, which draws custom designs onto the client’s skin.
Are you ready? Let’s tighten your seatbelts and get into this blog to explore what an FDM 3D printer is, its components, the benefits of its use, and how it works.
Table of Contents
What is a FDM 3D Printer?
An FDM printer is a common type of 3D printer that is used in additive manufacturing technology. Originally invented by S. Scott Crump in the late 1980s, these printers are now among the most trending 3D printers.
Unlike the traditional manufacturing process whereby an object is created by removing material from a solid block, FDM deposits a material layer to create an object.
It’s like putting a LEGO block piece by piece – each brick is put in place, one by another until the complete model is formed.
These printers do this by melting the thermoplastic material, and the filament, and extruding it through a nozzle that deploys heating to maintain the material in a molten state. As the filament cools, it solidifies, forming the desired shape (a 3D model).
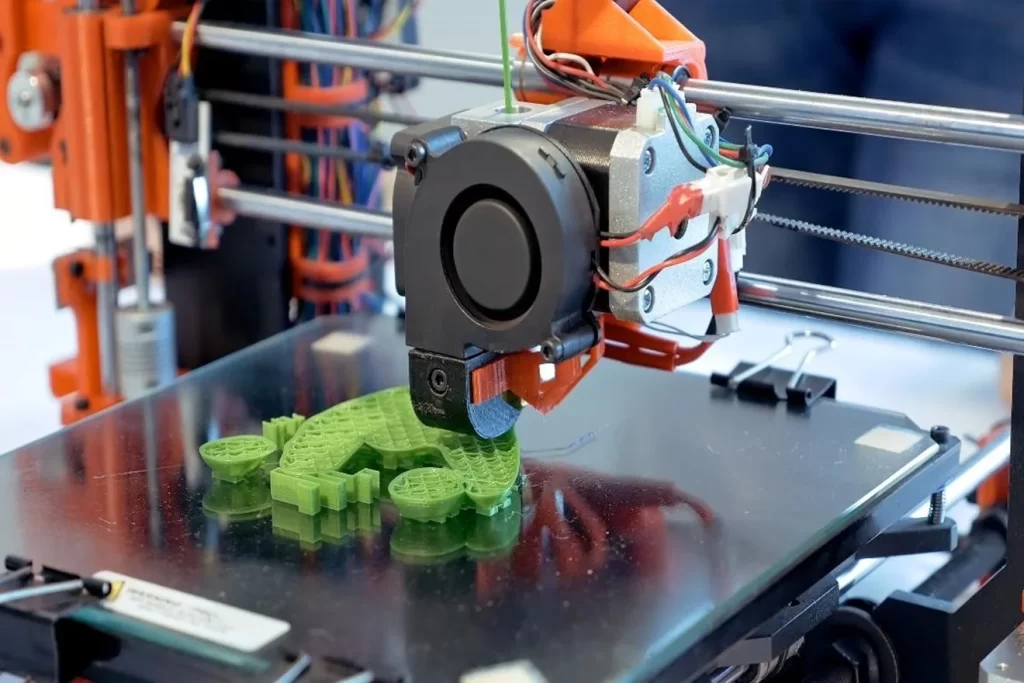
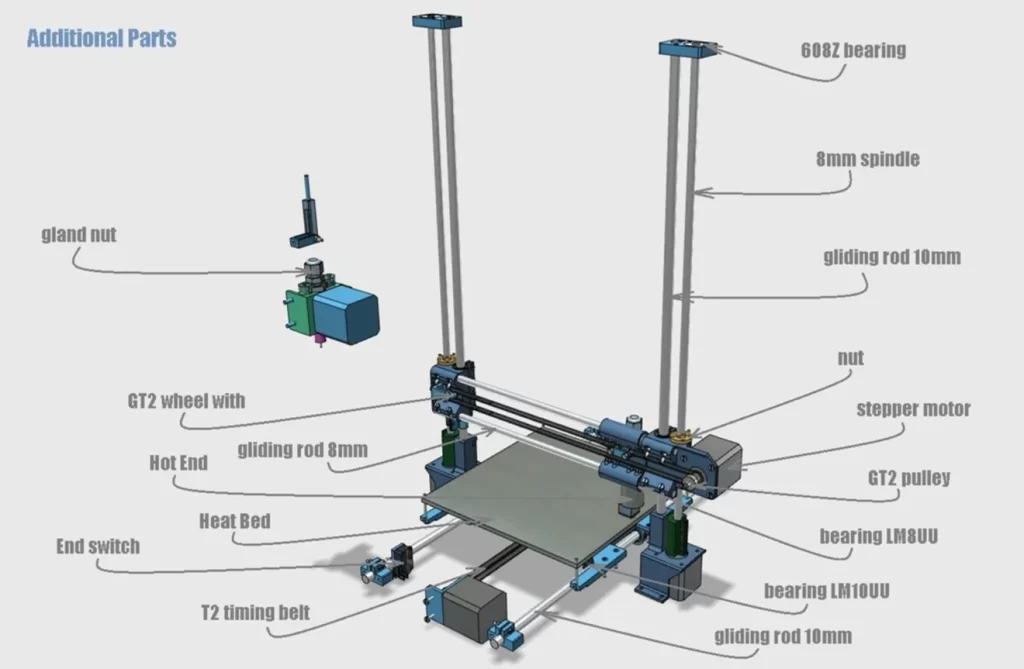
Main Components of FDM Printer
FDM printers have built-in several components that work together to create 3D objects. The main components that play a role in printing are:
- Extruder
The first extruder is the filament drive gear which forces the filament into the hot end. It is mainly regulated by a stepper motor that controls the filament flow most precisely.
The hot end has a heated block in which the filament is melted. It also has a nozzle through which the molten filament is extruded to create a continuous filament.
The nozzle diameter (1.75mm or 2.85mm) defines the thickness of the material extruded and affects the resolution of the print.
- Build Area (Print Bed)
This is the area where the 3D object is constructed layer by layer. It is often heated to help with adhesion and reduce warping, especially when printing with materials like ABS. The measurement is done in the XYZ dimension.
For example, 9 inches wide (X) by 9 inches deep (Y) by 11 inches high – 9x9x11 inches. More complicated prints are split into smaller parts that can be combined afterward.
- Stepper Motors
Stepper motors control the movement of the print head and the build platform. The X and Y motors move the print head horizontally, while the Z motor moves either the print head or the build platform vertically.
A separate stepper motor is typically used to drive the filament through the extruder.
- Cooling Fans
A fan cools the heat break, a section of the hot end, preventing the filament from melting too early and causing clogs.
Another fan directs air onto the freshly extruded filament to cool it rapidly, helping to improve print quality by reducing warping and improving layer adhesion. Not all 3D printing materials need active cooling but truly polish most 3D prints.
- LCD Screen or Interface
Most FDM printers come with a control panel in the form of an LCD screen or a touch screen where users can start a print, pause it, cancel it, change settings, and check on the printing process.
It cut off the need for a computer connected with software (Cura). But you have to insert an SD card in the printer to read the G-code instructions.
- Endstops
These are the sensors that detect when the print head has reached the end of its travel on each axis. They help in setting the home position for the printer, ensuring accurate and consistent prints.
How Does an FDM 3D Printer Work?
Now you have better know-how of all the components of an FDM printer. It’s time to get into the details of how it works:
Step 1: Designing the Model
The journey starts with a 3D model created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. Everything you want to print with a DFM printer is first printed in a digital blueprint, the same way we do with impact and non-impact printers.
This digital file is then converted into a format that the 3D printer translates to usually an STL or OBJ file.
Step 2: Slicing the Model
Once the design model is done, the next step involves jumping into slicing software. Here a 3D model is sliced into hundreds or thousands of thin layers. This software translates each layer into G-code language that instructs the printer.
Each layer represents a cross-section of the final object. The slicing software also generates the tool paths for a printer to follow and determines parameters such as infill density, print speed, and support structures.
Step 3: Printing the Object
3D printers melt a thermoplastic plastic material (fed into the printer), normally PLA, ABS, or PETG by heating it and forcing it through a heated nozzle.
The nozzle moves on the X and Y axes and extrudes the melted filament onto the build platform in thin layers.
Once a layer is completed, the build area or the nozzle moves along the Z-axis to print the next layer. This process repeats until the entire object is printed.
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
When the melted filament extrudes through the heated nozzles, the plastic cools instantly, solidifying onto the emerging part of the build platform. Some objects with complex designs may require temporary support during the printing process.
Once the process is done, this support is removed and set away in post-processing, leaving behind the intricately detailed design print.
Step 5: Post Processing
After the final printing layer is fully formed, the object may require post-processing, such as removing support structures, sanding, or painting, to achieve the desired finish.
That’s it! I have explained the whole working process. When the FDM 3D printer is in your hand, it’s super easy to convert the digital file into three-dimensional objects.
The appealing comb of design, technology, and materials science is what defines FDM 3D printing as a cornerstone of rapid prototyping and manufacturing.
Benefits of Using an FDM 3D Printer
- Affordability: FDM 3D printers are relatively affordable compared to other type of 3D printers. The materials used like PLA and ABS are also cheap, making them more affordable for hobbyists and small businesses.
- Versatility: FDM can work with a variety of thermoplastic materials, including ABS, PLA, PETG, and nylon. Whatever you want to print (simple prototypes or intricate designs of multiple colors), this printer can handle it all alone.
- Ease of Use: FDM printers are easy to use and maintain. Even a beginner can start printing designs with minimal setup and simple software.
- Speed: FDM can produce objects relatively quickly, especially for simple designs. This speedy prototyping makes it invaluable for industries where time is money.
Conclusion
FDM is one of the most popular and affordable 3D printing techniques that changed the way we design objects in this modern time. FDM printers are available for everyone, from hobbyists to students, or professional users of the device.
When you know A-Z about FDM printers (the printer’s components and how they work), the sky is the limit and your creativity can go as far as it can with FDM.
Follow the above steps and make your creation even better!
